Color Lab Effy Moom
Use our tool below to seamlessly convert between various color systems including CIELAB, HEX, sRGB, CMYK, and XYZ. To change your input values, simply select your desired system from the drop-down menu in the Settings section. Input. L (0 to 100) a (-128 to 128) b (-128 to 128) Output.

What is Lab Color in (Quick Facts & Guides)
Al crear escalas para éstos atributos, podemos expresar en forma precisa el color. El espacio de color L*a*b* fue modelado en base a una teoría de color oponente que establece que dos colores no pueden ser rojo y verde al mismo tiempo o amarillo y azul al mismo tiempo. Como se muestra a continuación, L*indica la luminosidad y a* y b* son las.
The Print Guide Tolerancing color in presswork CIE L*a*b* and DeltaE
Use the form below to convert color data across different color standards and color spaces (RGB, CMYK, L*ab, L*ch, L*uv, Hunter, XYZ etc.). Looking for color math or specific conversion formulas? Check our math page for some practical examples. If you are not sure how to start, check our practical step-by-step instructions. Select data type.
L*a*b* color space 3nh_colorimeter spectrophotometer_light box_gloss meter
The L*a*b* color space provides a more perceptually uniform color space than the XYZ model. Colors in the L*a*b* color space can exist outside the RGB gamut (the valid set of RGB colors). For example, when you convert the L*a*b* value [100, 100, 100] to the RGB color space, the returned value is [1.7682, 0.5746, 0.1940], which is not a valid.
La Be 0B8
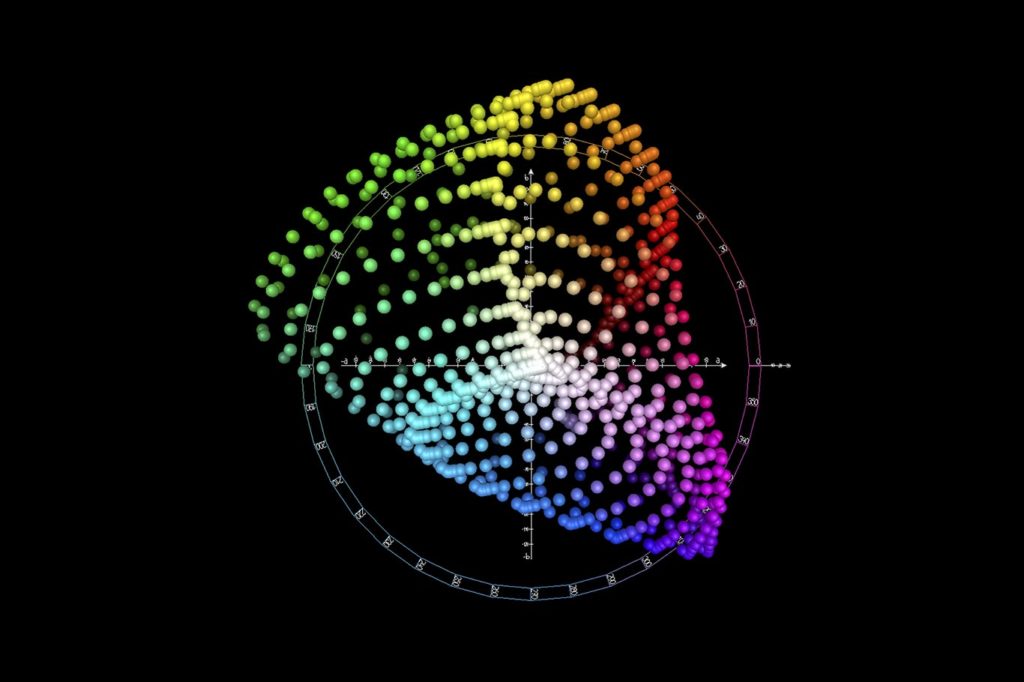
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as L*a*b*, is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. It expresses color as three values: L* for perceptual lightness and a* and b* for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow.

Graphical representation of the L*a*b* colour measurement system.... Download Scientific Diagram
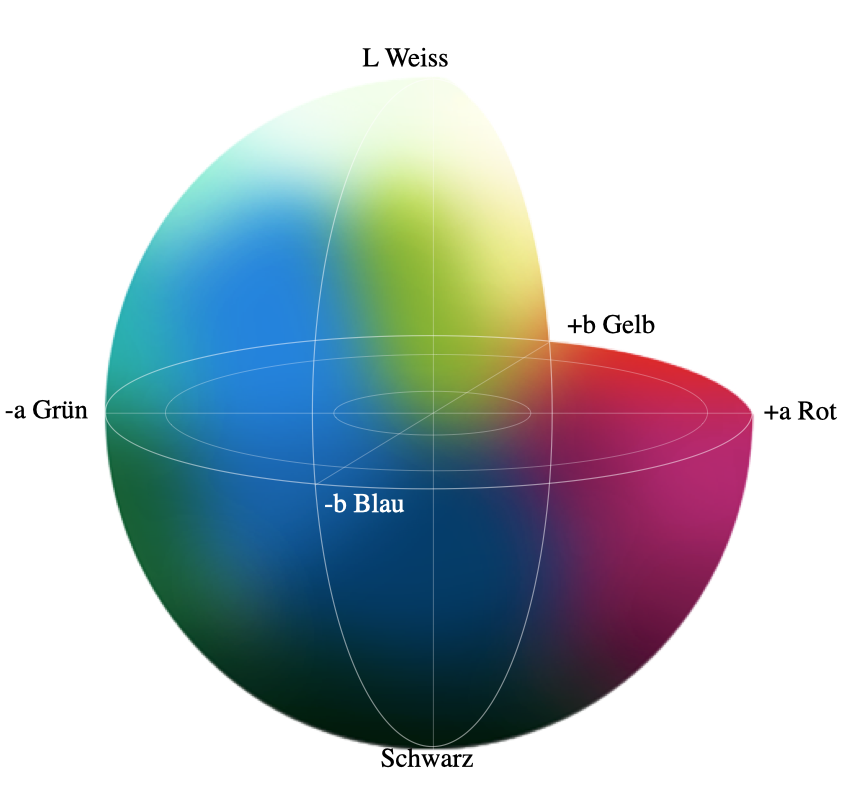
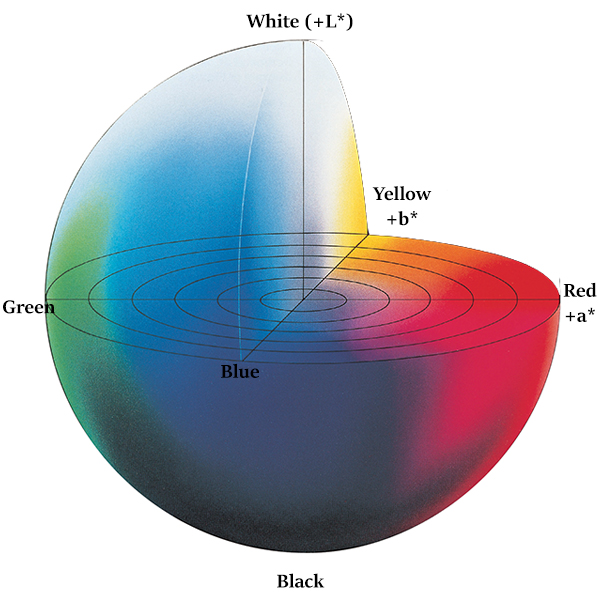
The CIELAB color space is organized in a cube form. The L* axis runs from top to bottom. The maximum for L* is 100, which represents a perfect reflecting diffuser. The minimum for L* is zero, which represents black. The a* and b* axes have no specific numerical limits. Positive a* is red.
Color Spaces
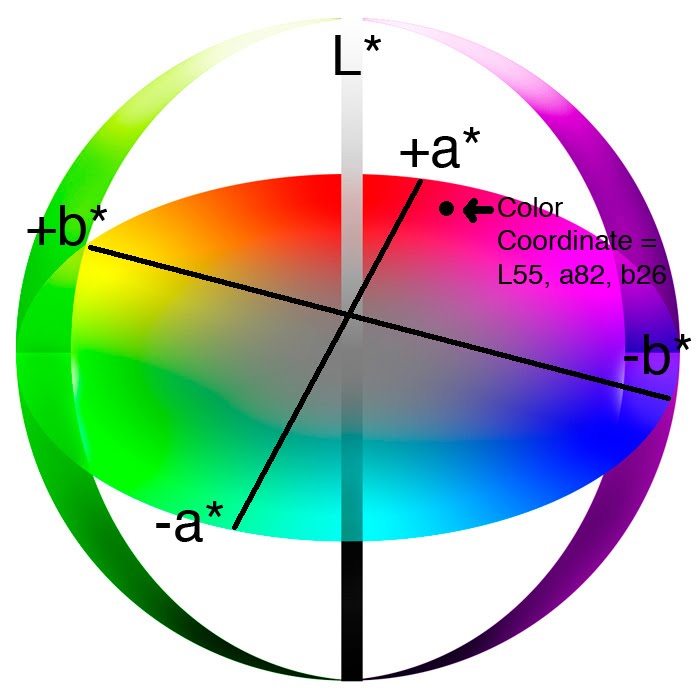
Along the b* axis, +b movement represents a shift toward yellow. The center L* axis shows L = 0 (black or total absorption) at the bottom. At the center of this plane is neutral or gray. To further demonstrate how L*a*b* values represent specific colors, see flowers A and B, below. We've also plotted their values on the CIELAB Color Chart above.

A representation of the CIE L*a*b* color space showing lightness (L*)... Download Scientific
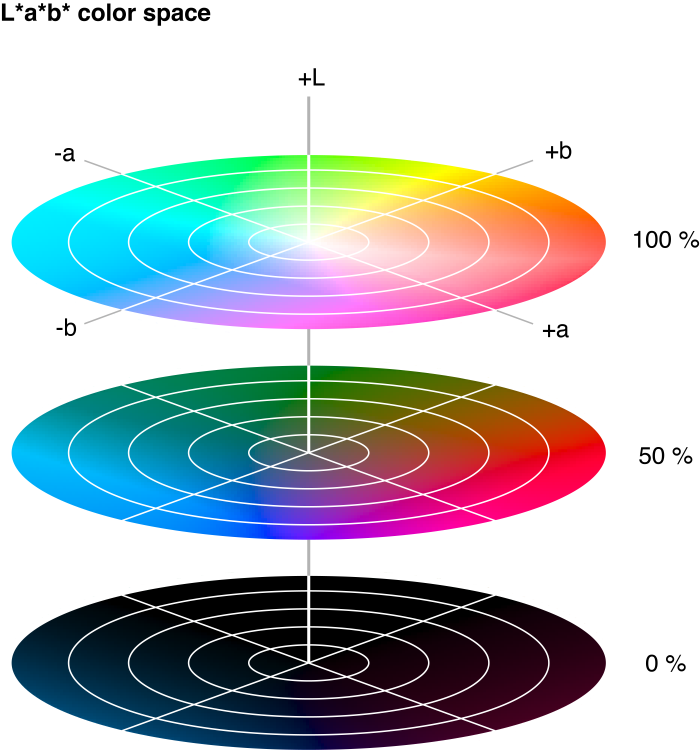
The color of (coated) objects is visualized and quantified by using the CIELAB color space. The 3-dimensional color space is built-up from three axes that are perpendicular to one another. The L* -axis gives the lightness: a white object has an L * value of 100 and the L * value of a black object is 0. The so-called achromatic colors, the.

The threedimensional CIE L*a*b* color space Download Scientific Diagram
This means that the a and the b are not representing one color but an axis of complementary colors. Two colors that, if mixed in this model, the cancel each other and make a neutral gray. So the scale is not 0 to 255 but -128 to +128 where the 0 is at the middle indicating that you have a gray.
Color spaces and color profiles what are they? The differences.
Lab Color is a more accurate color space. It uses three values (L, a, and b) to specify colors. RGB and CMYK color spaces specify a color by telling a device how much of each color is needed. Lab Color works more like the human eye. It specifies a color using a 3-axis system. The a-axis (green to red), b-axis (blue to yellow) and Lightness axis.

Enter the L*a*b*oratory Making Color Spatial
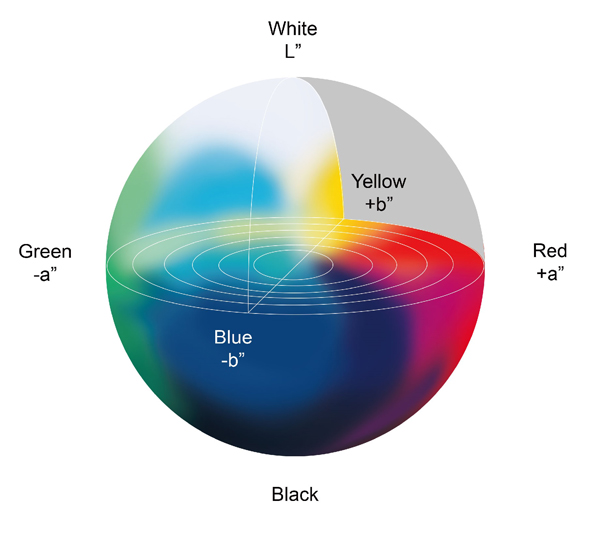
Hunter L,a,b color space is a 3-dimensional rectangular color space based on Opponent-Colors Theory. L (lightness) axis - 0 is black, 100 is white, and 50 is middle gray a (red-green) axis - positive values are red, negative values are green, and 0 is neutral

L*a*b* Color Space Examples for students Pinterest Colors, Blog and Globes
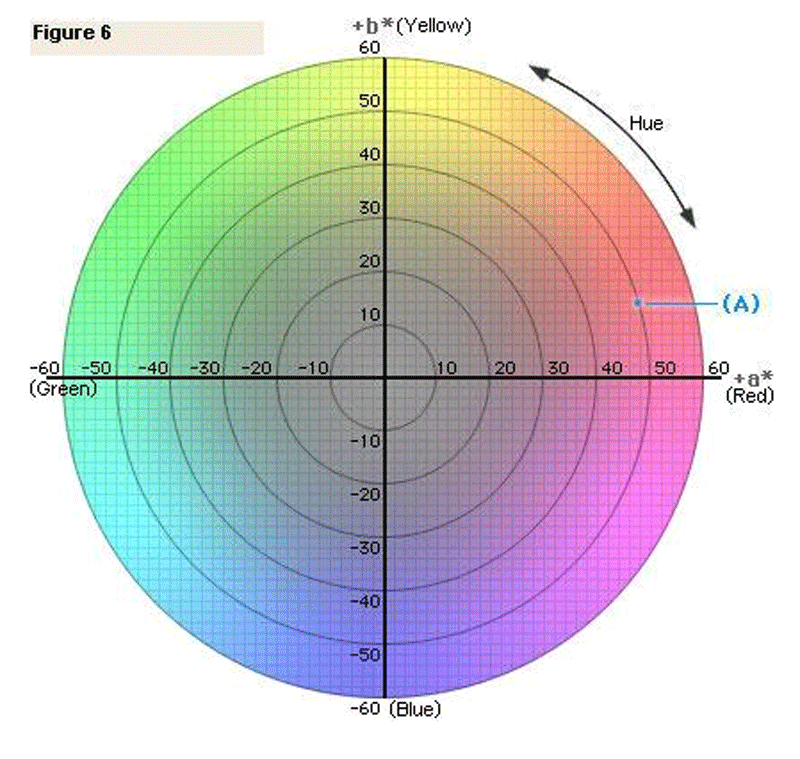
This color system represents the quantitative relationship of colors on three axes: The L* value indicates lightness, and a* and b* are chromaticity coordinates [11]. k is a constant representing.

CIE Lab L *, a * and b * color space Download Scientific Diagram
Color is an important aspect of coatings, and the color of a coating needs to match the desired specification. There are several ways to measure color, but one of the most common methods is the CIELAB color scale. The CIELAB color scale is a three-dimensional color model that was developed by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1976. It is based on the tristimulus values of a.
What Is CIE 1976 Lab Color Space? Konica Minolta Color, Light, and Display Measuring Instruments
To reproduce an exact desired color every time, manufacturers and designers need ways to quantify a color's properties and determine the numerical difference between shades. CIELAB or CIE L*a*b* is a device-independent, 3D color space that enables accurate measurement and comparison of all perceivable colors using three color values.

The L*a*b* model from CIELAB color space (Source HunterLab, Reston, VA). Download Scientific
Challenge: To choose the best color scale for the measurement. Hunter L, a, b and CIE 1976 L*a*b* (CIELAB) are both color scales based on the Opponent-Color Theory. This theory assumes that the receptors in the human eye perceive color as the following pairs of opposites. • L scale: Light vs. dark where a low number (0-50) indicates dark and.
How do We Define Accurate Color?|BenQ Singapore
Convert Lab to RAL, BS4800 BS 5252 and BS381C colours to NCS, Pantone, Dulux, Farrow and Ball, BS 2660 colours. Also into RGB and find close alternatives